
Nucleotides: The “Golden” Nutrient Supporting Immune Health and Sustainable Growth in Children
In the journey of raising healthy children, immunity is one of the top concerns for parents. A strong immune system is essential for children to grow up healthy—it acts as a powerful shield, protecting them from harmful agents and helping prevent illness not only in the present but throughout their life stages. So how can we build a strong immune system? While many factors contribute, recent scientific research has identified nucleotides as a key nutrient that plays a significant role in supporting immune health.
Let’s explore the fascinating benefits of nucleotides:
- What are nucleotides?
- How does the body produce nucleotides?
- Why are nucleotides important for the immune system, especially in children?
- What is the appropriate amount of nucleotide supplementation?
1. What Are Nucleotides?
Think of nucleotides as the “building blocks” of DNA and RNA—the essential components that form the structure of cells in the body. DNA and RNA are involved in countless physiological and biochemical processes, from protein and enzyme synthesis to energy production and cellular communication.
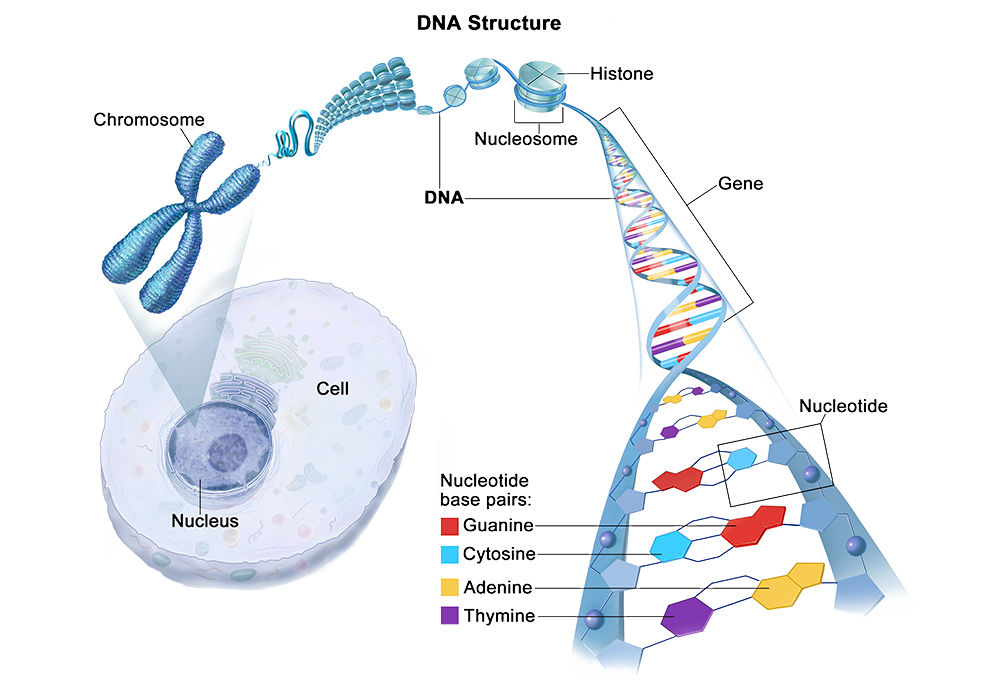
2. How Does the Body Produce Nucleotides?
The body synthesizes nucleotides through two main pathways: Endogenous synthesis (produced internally) and Dietary intake (from food). Previously, it was believed that endogenous synthesis was sufficient. However, recent studies have shown that dietary supplementation plays a crucial role—especially during periods of increased nutritional demand such as the first 1,000 days of life, puberty, illness, etc.
If the body lacks sufficient nucleotides or essential nutrients during these critical phases, internal synthesis may be compromised. Therefore, a balanced diet rich in nucleotides is essential not only for children but also for adults.
3. Unlocking the “Hidden Power” of Nucleotides for Overall Health
Nucleotides contribute to the development and efficiency of immune cells, especially in children whose immune systems are still maturing. They support immunity in several ways:
3.1 Enhancing Immune Cell Production and Function
As the raw material for DNA and RNA synthesis, nucleotides help build immune cells—boosting both their quantity and quality. For example, nucleotides support the production and function of T and B lymphocytes, which act as “soldiers” defending the body against pathogens.
One study showed that children who consumed formula enriched with nucleotides had significantly higher antibody responses to flu and diphtheria vaccines compared to the control group.
3.2 Strengthening the Gut Barrier and Optimizing Gut Microbiota
Did you know that about 70% of immune cells are located in the gut? A healthy gut not only protects against external threats but also supports digestion and nutrient absorption—key to sustainable growth.
Nucleotides help repair the gut lining and nourish beneficial bacteria, limiting the growth of harmful microbes and maintaining digestive function.
A meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that nucleotide supplementation significantly reduced the incidence of diarrhea and gastrointestinal infections in children.
3.3 Supporting Physical Development and Sustainable Growth
During early childhood, the body undergoes rapid growth and cell formation, requiring a steady supply of nutrients. Nucleotides—composed of Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine, and Uracil—play a vital role in protein synthesis, helping build strong muscles and bones and laying the foundation for healthy physical development.
Shape
4. Where Are Nucleotides Found and How Much Should Children Consume?
Nucleotides naturally occur in many foods, especially:
- Breast milk: The ideal source for infants, containing up to 100 μmol/L of nucleotides.
- Meat, fish, and legumes: Red meat, poultry, seafood, soybeans, and peas contain 0.003–17g per 100g of food.
- Vegetables: Mushrooms, broccoli, spinach, and other vegetables may contain up to 4g per 100g.
- Milk and dairy products: Rich in nucleotides and widely available.
Studies agree that adding up to 7.2mg of nucleotides per 100ml of infant formula is safe and effective for boosting immunity.
In special cases—such as illness, malnutrition, premature birth, or lack of breastfeeding—supplementing nucleotides through specialized nutritional products is a necessary solution to support digestive health, immunity, and overall well-being.
“To ensure children receive adequate nucleotides and other essential nutrients for healthy development, parents should:
– Exclusively breastfeed for the first 6 months and continue breastfeeding with complementary feeding until age 2.
– Provide a balanced and diverse diet rich in nucleotide-containing foods.
– Consult a pediatrician or nutrition expert for guidance on appropriate supplementation.”
— Dr. Ho Thi Nam Hue, Vinamilk Nutrition Center – An Khang General Clinic
Shape
Conclusion
Nucleotides are a “golden” nutrient closely linked to children’s immune health. Supplementing nucleotides through diet or specialized nutrition helps build a strong immune system, reduce illness risk, and support comprehensive development—empowering children to explore the world with confidence.
We hope this article has provided valuable and reliable insights about nucleotides. Let’s join hands with Vinamilk to support the health and holistic development of Vietnamese children!
Dr. Ho Thi Nam Hue, Vinamilk Nutrition Center – An Khang General Clinic
Reference
[1]. 2020 by Katherine R. Mattaini. Nucleotides and nucleic acids. In Biology 103: Introduction to Biology. Link
[2]. Giuliani AL, Sarti AC, Di Virgilio F. Extracellular Nucleotides and nucleosides as signalling molecules. Immunol Lett. 2019 Jan;205:16-24. Link
[3]. Cheng, Z. (Ed.). (2020). Nutritional signaling pathway activities in obesity and diabetes. Royal Society of Chemistry.. Link
[4]. Ding, T., Song, G., Liu, X., Xu, M., & Li, Y. (2021). Nucleotides as optimal candidates for essential nutrients in living organisms: A review. Journal of Functional Foods, 82, 104498. Link
[5]. Carver, J. D. (1999). Dietary Nucleotides: effects on the immune and gastrointestinal systems. Acta Paediatrica, 88, 83-88. Link
[6]. Maldonado, J., Navarro, J., Narbona, E., & Gil, A. (2001). The influence of dietary Nucleotides on humoral and cell immunity in the neonate and lactating infant. Early human development, 65, S69-S74.
[7]. Schaller, J. P., Kuchan, M. J., Thomas, D. L., Cordle, C. T., Winship, T. R., Buck, R. H., ... & Wheeler, J. G. (2004). Effect of dietary riboNucleotides on infant immune status. Part 1: Humoral responses. Pediatric research, 56(6), 883-890. Link
[8]. Deborah Pedersen, MD, MS, Allergy & Asthma Care, PC, Taunton, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team (Review Date 3/31/2024). Link
[9]. Gutiérrez-Castrellón P, Mora-Magaña I, Díaz-García L, Jiménez-Gutiérrez C, Ramirez-Mayans J, Solomon-Santibáñez GA. Immune response to nucleotide-supplemented infant formulae: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2007 Oct;98 Suppl 1:S64-7. Link
[10]. Wiertsema SP, van Bergenhenegouwen J, Garssen J, Knippels LMJ. The Interplay between the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System in the Context of Infectious Diseases throughout Life and the Role of Nutrition in Optimizing Treatment Strategies. Nutrients. 2021 Mar 9;13(3):886. Link
[11]. Uauy, R., Quan, R., & Gil, A. (1994). Role of Nucleotides in intestinal development and repair: implications for infant nutrition. The Journal of Nutrition, 124, 1436S-1441S. Link
[12]. Singhal, A., Macfarlane, G., Macfarlane, S., Lanigan, J., Kennedy, K., Elias-Jones, A., ... & Lucas, A. (2008). Dietary Nucleotides and fecal microbiota in formula-fed infants: a randomized controlled trial. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 87(6), 1785-1792. Link
[13]. Yang L, Guo Z, Yu M, Cai X, Mao Y, Tian F, Xu W, Liu G, Li X, Zhao Y, Xie L. Profile of Nucleotides in Chinese Mature Breast Milk from Six Regions. Nutrients. 2022 Mar 29;14(7):1418. Link
[14]. Thorell L, Sjöberg LB, Hernell O. Nucleotides in human milk: sources and metabolism by the newborn infant. Pediatr Res. 1996 Dec;40(6):845-52. Link [15]. National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Nucleotide. In NCI Dictionary of Genetics Terms. [Link]